
When a transaction fails, the standard industry response is often to initiate a retry. There are, however, rules imposed by the card schemes that limit the retries attempts within a certain window period. PayPal quotes that up to 15 reattempts are permitted by Visa within a 30-day period for certain decline categories. Whilst Mastercard retries are limited to 10 in a 24-hour period. Exceeding these thresholds can result in fines, reaching into the thousands.
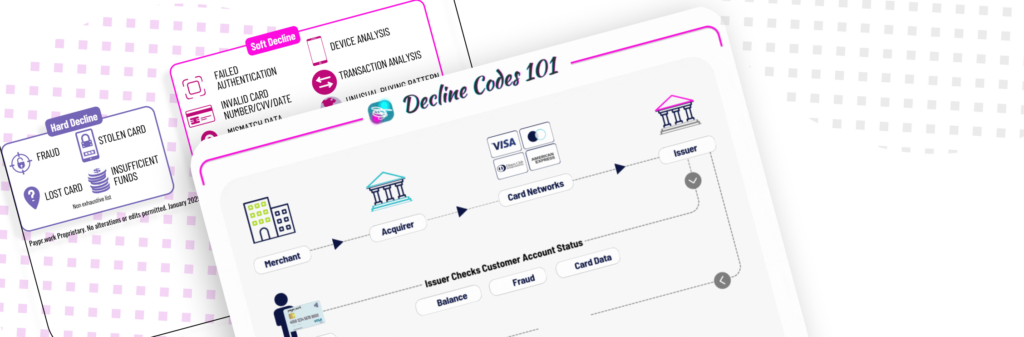
The approvals and rejections that merchants get from an authorisation request typically come in the form of 2-digit or 3-digit response codes, with each code indicating the reason a particular transaction is accepted or declined. The declined codes are categorised as 2 types:
◾Hard – the transaction cannot be reattempted
◾Soft – the transaction can be retried
But in fact, there’s more to it. There are a number of codes that are sitting in a shade of grey and can be prone to confusion… For example, “Do Not Honor” is a catch-all decline code used when an issuer rejects a transaction without providing a specific reason. This rejection could stem from various issues, which could lead to different fallback strategies, yet the code itself offers no clarity, leaving merchants guessing and, in many cases, shoppers frustrated by the failed transaction.
There’s a multi-layered process guiding how these codes flow, which, in my view, really highlights the confusion and challenges to not only interpreting these seemingly simple digits and but also managing all the technical details, rules, and processes involved.
◾Issuer: the response codes are issued by the issuing bank based on the customer’s account status, such as insufficient funds, transaction limits, or suspected fraud.
◾Card Networks: they receive and standardise these codes under industry norms, although slight variations can exist at network levels.
◾Acquirers/Payment Systems: they further refine the codes, grouping them in a way to give merchants clearer insights into decline reasons.
◾Merchant-Level Actions: based on these refined codes, the merchants then implement different strategies that may involve intelligent payment retries.
Understanding the declines root causes is crucial for determining the most effective actions to reduce lost sales and enhance the overall payment experience.
Paypr.work blends payment knowledge and custom research into a simplified yet insightful narration. Our narratives feature visually engaging designs that break down both fundamental and complex payment jargons into bite-sized, repetitive micro-concepts to promote better comprehension and retention.
Sign up for a Paypr.work Premium Membership to exclusively access all of our payment resources, including our full articles, industry insights, ecosystem maps, reports, videos, and our unique library of bespoke infographics.
Don’t miss out— sign up to learn payments in a captivating way!


You have provided so much light and knowledge in a fascinating world. You definitely bring the fun to Fintech like no one else and actually know what you are talking about! Thanks goodness for you😁!

Vice President Global Product Expansion, Shift4
Impressive, congratulations Sandra and Team Paypr.work. The detail in each of your 100+ infographics is outstanding and showcases your expertise well… Continued success for this remarkable work!

LinkedIn Strategist | Digital Transformation Leader

Host of Heads Talk
Your diagrams have the ability to explain the most complicated of topics in way that can be understood by anyone. Not many people have the ability to create self-explanatory visuals, so keep doing your magic 🔥🔥🔥!

CEO & Co Founder of CLOWD9
Your content is so informative, accurate, and fabulously presented in infographics that always attract great attention. Your visuals naturally spark strong engagement regardless of the LinkedIn algorithms !

B2B Marketing, Marqeta
The depth of Paypr.work knowledge and skill sets are truly impressive. Their ability to combine deep industry expertise with well-depicted visual is pretty unique. I strongly recommend Sandra and Paypr.work !

Director EMEA Payment Solutions, Marriott International
👏👏 👏👏 👏👏 I always love your content and in fact, I am so happy for all of us in the industry… we’re lucky to have you sharing your payment wisdom with us 🤓… thank you! Keep up the great work.

Strategic Accounts Director, Truelayer | Payments and Fintech Geek
Merci Sandra pour ta facilité à vulgariser le paiement via de simples dessins, qui me surprendront toujours. Pour ceux qui ne connaissent pas son travail, je vous invite à suivre Paypr.work [ˈpeɪpəwəːk]!

Product Manager Paiement, Maisons du Monde
Your enthusiasm and ability to simplify Payments is so refreshing and literally shines through! Sandra and her team research, write content and create some stunning infographics for the payments industry….

Chief Operations Officer, Clowd9
Keep up the good work and know that your hard work and dedication is so inspiring for all of us. You are truly doing an incredible job and your consistent efforts don’t go unnoticed.

Chief Community Officer, NORBr | Redefining Payment Infrastructure | Linkedin Top Voice
Your posts are a masterclass in how payments have evolved from a basic utility to a strategic asset. Your ability to simplify this complexity and provide strategic direction along with implementation support is so invaluable. The clarity and depth you provide are exactly what this fast-evolving industry needs.

Chief Commercial and Operations Officer, Soffid
The mechanics of all things payment are a black box for most industry stakeholders. With the help of their well researched and designed infographics, Sandra and her team at Papr.work demystify complex flows and create awareness about the factors that play a role in the end to end processes.

Paul van Alfen | Managing Director Managing, Up in the Air - Travel Payment Consultancy
Your Paypr.work subscription gets you full access to all Paypr.work content in 1 place including: our weekly new payments articles, our infographic blog, exclusive discounts on all the services that Paypr.work has to offer and the opportunity to collaborate on free infographic to promote your knowledge/value proposition and more. The content is for personal use and cannot be copied, reproduced, redistributed, altered, modified, shared publicly or with third-party nor can derivatives of the work be created. The user may share content that is available through the free blog access subject to crediting Paypr.work with the attributions.